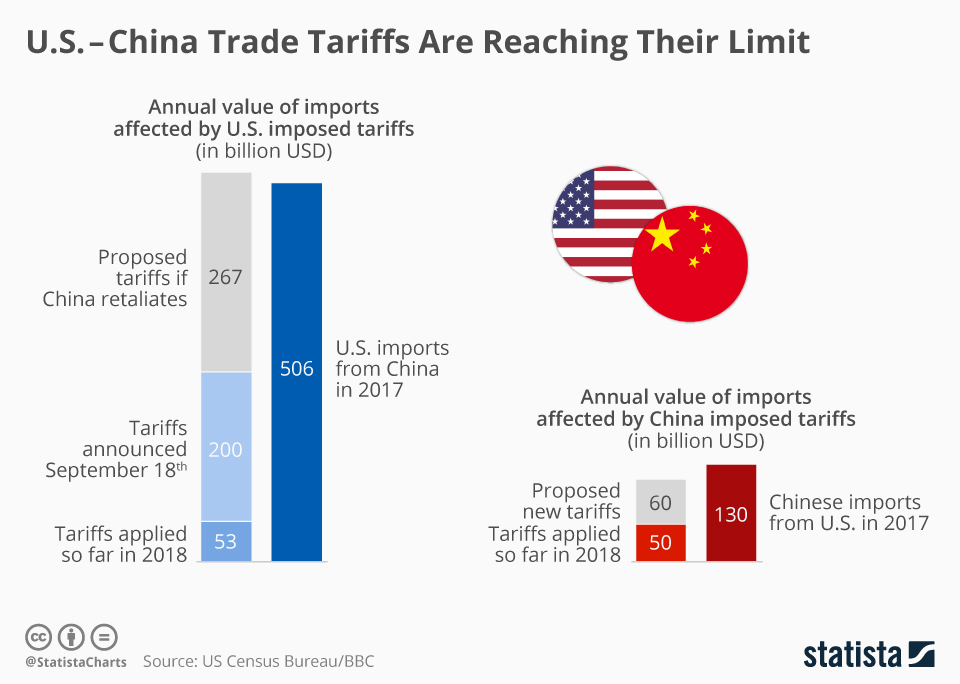
U.S.-China tariffs have emerged as a crucial aspect of international trade, especially in the context of recent geopolitical tensions. As the U.S. considers imposing stricter tariffs on Chinese imports, analysts warn of profound effects on both economies. These tariffs could increase prices for American consumers, exacerbating existing supply chain issues and leading to unintended consequences for the U.S. economy. Moreover, such actions could provoke retaliatory measures from China, straining an already fragile state of China trade relations. Understanding the full impact of U.S.-China tariffs requires a nuanced look at the implications for global markets and future economic partnerships.
Trade restrictions imposed on China, particularly in the form of tariffs, have sparked widespread debate regarding their potential implications for both nations. With concerns ranging from elevated consumer prices in the U.S. to the reshaping of global supply chains, the stakes are high. Economists are particularly focused on how these punitive measures might not only destabilize China’s economy but also create lasting challenges for American businesses and consumers. As we analyze the dynamics of U.S.-China trade relations, it’s essential to recognize the complexities involved in tariff policy and its potential to complicate diplomatic ties.
The Implications of U.S.-China Tariffs on Domestic Prices
The anticipated implementation of U.S.-China tariffs could lead to a significant increase in consumer prices across various sectors in the American economy. As tariffs rise, manufacturers are likely to pass these costs onto consumers, leading to higher prices for everyday goods, from electronics to clothing. This phenomenon may not just be a temporary spike; economists warn that persistent inflation could become a real issue, affecting the purchasing power of average Americans. Furthermore, products sourced from China, which account for a substantial portion of U.S. imports, are likely to experience marked price hikes, pushing consumers toward more expensive alternatives from other countries.
Moreover, the implications extend beyond just price increases. Tariffs could disrupt supply chains that rely heavily on Chinese goods, causing delays in production. Businesses may struggle to find alternative suppliers who can meet their demands at a reasonable cost and timeframe. This could further exacerbate inflation as companies grapple with increased operational expenses and seek to recoup losses through raised prices for their products. The interconnected nature of global supply chains means that problems in U.S.-China trade relations could have ripple effects, ultimately hurting consumers and businesses at home.
Supply Chain Disruptions and Economic Fallout
The potential for U.S.-China tariffs to cause supply chain disruptions cannot be overstated. As companies have optimized their supply chains for efficiency, many have come to rely on Chinese manufacturing for critical components. The swift implementation of substantial tariffs could force these manufacturers to rethink their sourcing strategies, resulting in delays and potential shortages. Sectors like electronics and automotive, which depend heavily on timely delivery of parts from China, are particularly vulnerable. As a result, businesses might face production halts or delays, leading to reduced output and, ultimately, job losses.
Economists have expressed concern that the repercussions of these disruptions may lead to a broader economic fallout. Increased tariffs could challenge labor markets too, as companies might look to offshore labor or relocate manufacturing away from China to avoid steep import costs. This could result in job losses in industries reliant on Chinese imports, ultimately affecting U.S. employment figures and economic growth. Moreover, the threat of supply chain issues compels more firms to stockpile goods or diversify their suppliers, further straining global supply networks and complicating trade relationships.
Reviving China-U.S. Trade Relations Amidst Tariffs
Despite the clamor surrounding tariffs, there’s a perspective that argues for the need to revive China-U.S. trade relations. Economists suggest that, rather than escalating tensions, both nations could benefit from entering into pragmatic negotiations aimed at crafting a mutually beneficial framework. Previous iterations of trade agreements, like the Phase One deal, showed that cooperation can yield positive results for both sides. If new tariffs provoke economic pain, it may motivate policymakers to seek dialogue, finding common ground in shared economic interests.
On the Chinese front, there’s a growing realization that improving trade relations with the U.S. is vital for sustaining economic growth amid declining revenues from exports. With the domestic economy facing challenges, an amicable trade relationship with the U.S. could mitigate some adverse effects of potential tariffs. However, for this to happen, the U.S. must approach negotiations knowing that tariffs can be leveraged as tools for bargaining, leading to more robust agreements that address fundamental issues in U.S.-China trade relations.
Long-term Effects of Tariffs on U.S. Economy
The long-term effects of implementing stiff U.S.-China tariffs extend far beyond immediate retrenchments in trade; they could reshape the U.S. economy’s very fabric. Consider that expanding tariffs might initially insulate domestic manufacturers by shielding them from foreign competition. However, in the long run, such isolation may stifle innovation and efficiency, leading U.S. firms to rest on their laurels rather than adapting to a competitive global marketplace. Over-reliance on prototyping and manufacturing within the U.S. could cause such companies to become laggards in technology and creativity.
Moreover, as relationship dynamics between the U.S. and China become strained, the U.S. could find itself in a precarious position in global geopolitics. Economists point out that further tariff escalation could alienate other global partners who may perceive these actions as a unilateral exertion of power. Consequently, this could lead to a re-aligning of international trade agreements, with countries seeking more stable partnerships, perhaps leaning towards China in the absence of favorable conditions from the U.S. Ultimately, ignoring these long-term ramifications could set the U.S. economy on a treacherous path.
The Future of Global Trade Post-Tariff Era
In the wake of aggressive U.S.-China tariffs, the global trade landscape is poised for transformation. Companies worldwide may seek to diversify their supply chains to mitigate risks associated with heavy dependence on any single nation. Nations like Vietnam and India could seize this opportunity to become preferred trade partners, creating a shifting dynamic that may impact commodity flows, labor markets, and overall investment patterns. Many industry experts suggest that a redistribution of global trade could potentially spur innovation in countries traditionally overshadowed by Chinese manufacturing prowess.
However, this evolution may not occur without significant challenges. Establishing new supply chains and trade arrangements is often complicated and time-consuming, requiring companies to invest substantial resources to adapt to new manufacturing locales and regulatory environments. For instance, quality control problems, logistical obstacles, and different standards could surface, leading to inconsistency across markets. As countries like Vietnam grow into the manufacturing powerhouses of the future, the transition will require strategic support from their governments to attract necessary investments and ensure competitiveness.
China’s Response to New Tariffs: Strategic Adjustments
As the threat of new tariffs looms, China is altering its economic strategies to prepare for potential fallout from U.S.-imposed tariffs. This involves adopting countermeasures aimed at securing its economy against the loss of U.S. imports, including promoting local consumption and diversifying its trading partnerships. Chinese policymakers have been vocal about the need to bolster domestic markets and stimulate economic activity as a means to reduce reliance on U.S. exports, which have historically been a cornerstone of China’s economic strategy.
In addition to internal adjustments, China is actively seeking to strengthen ties with other major economies, including those in the European Union, to offset economic vulnerabilities. By fostering relationships with global partners through initiatives like the Belt and Road Initiative, China aims to mitigate the impact of U.S. tariffs on its economy. As Beijing engages in diplomatic efforts to broaden its influence, it signifies that even amid tariff-induced pressures, there are opportunities for strengthening China’s trade position on the world stage.
Possible Winners and Losers from Trade Policy Changes
The onset of new U.S.-China tariffs raises the critical question of who stands to benefit from these trade policy changes. While the U.S. aims to protect domestic manufacturers, certain countries may actually benefit from a decline in Chinese imports. Nations such as India and Vietnam are in prime positions to bridge the gaps left by Chinese exports. With global supply chains undergoing a radical transformation, competing countries could potentially attract new investments, reducing U.S. dependency on China over time.
However, potential winners are not without their caveats. These nations will need to ramp up their production capabilities, improve quality standards, and develop the necessary skills in their workforce to truly capitalize on the opportunities presented by the shift in trade patterns. It is unlikely that they can fully replace China’s vast manufacturing capabilities overnight. Therefore, while there may be winners in this evolving scenario, the transition is fraught with challenges that need careful navigation.
Economic Risks from Tariffs: A Broader Perspective
The economic risks posed by introducing stiff tariffs between the U.S. and China warrant a broader perspective, particularly when evaluating the long-term effects on international relations and economic stability. While the immediate ambition may be to address trade imbalances, there’s a palpable risk that such protectionist measures could trigger retaliatory actions from China, which may lead to an escalating trade war. This escalation could undermine the long-standing economic ties that benefit both nations, fostering resentment that might extend beyond the realm of trade into diplomatic relations.
Furthermore, the impact of tariffs is not confined to the borders of the U.S. or China; it could potentially destabilize the global economic landscape. International markets thrive on predictability and stability, and if tariffs are perceived as unilateral moves by the U.S., other nations may scramble to adjust their trade agreements. The resultant instability could set off a chain reaction affecting global supply chains, leading businesses worldwide to adapt abruptly, resulting in uncertain economic climates that could last for years to come.
Navigating Foreign Trade Relationships Under U.S. Tariff Policies
As the U.S. embarks on a firmer stance regarding tariffs, navigating foreign trade relationships will become increasingly complex. Countries that have traditionally aligned themselves with the U.S. may find themselves caught between competing interests, particularly if they are also engaging in trade with China. The delicate balance of maintaining beneficial ties with the U.S. while not alienating China poses significant challenges for other nations, and many will need to tread lightly. This unpredictability will likely require a re-evaluation of trade agreements and partnerships to ensure that they are insulated from ramifications of U.S. policies.
In addition, economic analysts underscore the importance of transparent communication between nations to mitigate the risks of misunderstanding and potential trade conflicts. As nations navigate these turbulent waters, cooperation and dialogue become essential tools in maintaining economic stability. By fostering transparent discussions about tariff implications and trade strategies, countries can work towards minimizing disruption while optimizing trade relationships during an unpredictable period in global economic history.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the potential effects of U.S.-China tariffs on the U.S. economy?
U.S.-China tariffs can lead to higher prices for American consumers, disrupt supply chains, and potentially create labor shortages. They might also provoke a currency war with China and negatively impact overall U.S. economic stability.
How could Trump’s proposed tariffs on China affect trade relations?
Trump’s proposed tariffs on China could strain U.S.-China trade relations further, possibly leading to renewed negotiations but also providing China opportunities to strengthen ties with other global allies, complicating diplomatic dynamics.
What impacts do China tariffs have on U.S. supply chains?
China tariffs can significantly disrupt U.S. supply chains by increasing production costs, leading to delays, labor shortages, and a need for businesses to find alternative suppliers or manufacturing bases, which may not align with existing supply chain infrastructures.
How might U.S.-China tariffs influence prices for American consumers?
U.S.-China tariffs generally lead to an increase in prices for American consumers as companies pass the added costs of tariffs onto consumers, making imported goods more expensive.
What are the long-term consequences of increased U.S. tariffs on Chinese imports?
The long-term consequences could include destabilizing the Chinese economy, altering global supply chains, and risk shifting production to countries that may not have the capacity to meet U.S. demand effectively, which could take years.
How have previous U.S.-China tariffs impacted global trade dynamics?
Past U.S.-China tariffs have restructured global trade dynamics by prompting businesses to seek alternative markets, impacting countries like Vietnam and Mexico, and shifting focus towards developing new trade relationships outside China.
In what ways could new tariffs deepen U.S.-China economic tensions?
New tariffs could deepen tensions by encouraging retaliatory measures from China, worsening diplomatic relations, and causing a broader trade war that may lead to long-term economic repercussions for both nations.
What strategies has China implemented to cope with U.S. tariffs?
In response to U.S. tariffs, China has focused on stimulating domestic consumption, seeks new markets through initiatives like the Belt and Road Initiative, and aims to enhance trade relations with other countries to mitigate dependency on the U.S.
Can other countries fill the gap left by reduced Chinese imports due to U.S. tariffs?
It is challenging for other countries to quickly fill the gap left by reduced Chinese imports, as China has established itself as a dominant manufacturer. Countries like India and Vietnam could play a role, but they face significant hurdles in scaling up their production capabilities.
What are the potential geopolitical repercussions of U.S.-China tariffs?
U.S.-China tariffs may result in geopolitical shifts, with China potentially leveraging its position to strengthen alliances with other nations affected by similar tariffs, thereby reshaping international trade partnerships.
| Key Point | Details |
|---|---|
| Impact on China’s Economy | Imposing tariffs could worsen the already struggling Chinese economy, leading to decreased exports and exports to the U.S. |
| Effects on U.S. Consumers | Higher tariffs would likely lead to increased prices for American consumers and disrupt supply chains. |
| Strategic Response from China | China views the potential tariffs as an opportunity for negotiations, but also has concerns over the impact on its exports. |
| Potential Shift in Trade Alliances | Higher tariffs may lead China to strengthen ties with U.S. allies such as the EU, UK, and Japan to counteract U.S. actions. |
| Emerging Markets | China is looking beyond the U.S. and fostering markets in Southeast Asia, Latin America, and Sub-Saharan Africa. |
| Challenges for New Suppliers | Countries like India and Vietnam may benefit from a decrease in Chinese exports to the U.S., but infrastructure challenges remain. |
| Risks to U.S. Relations | A broad tariff strategy could push China and Europe closer together, weakening U.S. influence. |
Summary
U.S.-China tariffs are poised to have significant repercussions not just for the economies of both nations, but also for global trade dynamics and alliances. As discussions around imposing steep tariffs intensify, it becomes crucial to understand the potential consequences such actions could have on pricing, supply chains, and diplomatic relationships. If not approached carefully, U.S.-China tariffs may inadvertently strengthen Beijing’s relationships with U.S. allies while harming American consumers.